BrdU assay
Summary
BrdU is a synthetic nucleoside analog, like the nucleoside thymidine, except the methyl group is replaced with a bromine atom. BrdU can be incorporated into DNA whenever thymidine normally would be, including during DNA replication and repair. Therefore, BrdU is often used to label cells that are undergoing or have recently undergone DNA replication.
Also known as:
Bromodeoxyuridine assay, 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine assay
Samples needed
Live cells are treated with BrdU, which incorporates into DNA being replicated. Subsequent steps depend on how sample will be visualized, for instance by immunofluorescence microscopy or immunohistochemistry (add link).
Controls
Often times, controls for BrdU assays are not shown in published work.
Method
Cells are treated with BrdU for a defined length of time. Any cells undergoing S-phase within the window when BrdU was present will have BrdU incorporated into their DNA. BrdU can be recognized by an anti-BrdU antibody, then visualized by the desired method. In order for BrdU to be accessible for the antibody to bind, the DNA has to be denatured.
Interpretation
Add more later, but basically if a cell is positive, it was going through S phase when BrdU was present.
Special cases
To assess formation of single-strand DNA (ssDNA)
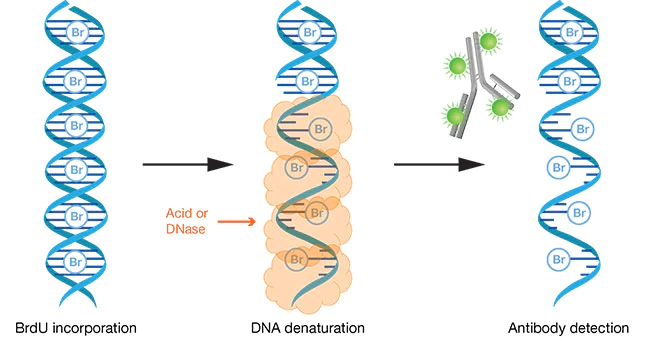
Normally, DNA has to be denatured for the BrdU antibody to detect any BrdU incorporated into the DNA (see Figure 1). However, if a) BrdU labeling occurs over a long period so that all DNA is labeled and b) BrdU staining is performed under non-denaturing conditions, the only BrdU that will be accessible to the antibody will be in areas where DNA is single-stranded for some other reason (besides denaturing), like replication fork collapse. So, in this case, staining correlates with the amount of ssDNA in a sample.
Figure 1. Once BrdU is incorporated into a piece of double stranded DNA (dsDNA), the DNA must be denatured in order for the anti-BrdU antibody to have access to bind BrdU. “Figure 1. BrdU staining with antibody detection.” by ThermoFisher Scientific. [Image Description]
Image Descriptions
Figure 1 image description: A diagram showing three steps in a BrdU assay. First, BrdU is incorporated into the dsDNA. Second, the DNA is denatured using acid or RNAse so that the BrdU is now accessible. Third, antibodies are added, and can now reach the BrdU and bind to it. [Return to Figure 1]
Phase of the cell cycle when DNA replication occurs (DNA synthesis phase)
A protein that binds very specifically to a protein of interest, normally produced by an organism's adaptive immune system to protect against pathogens, but also used in a variety of biotechnological applications
In reference to proteins, the loss of all structure except primary structure; in reference to nucleic acids, separation into individual strands with no base-pairing